Recently I been in a tech chat and was discussing the hashmaps and concurrent hashmap particularly, maybe I couldn’t explain it well and got the slap like a Superman got below. Here in this post I’m trying to explain basics again and few pics which let you know how they work exactly. concurrenthashmap has developed more complex recently till java 12 but we will look at only basic operations to know its foundation.

Unlike the HashTables where every read/write operation needs to acquire the lock, there is no locking at the object level in ConcurrentHashMap and locking is much granular at a hashmap bucket level.
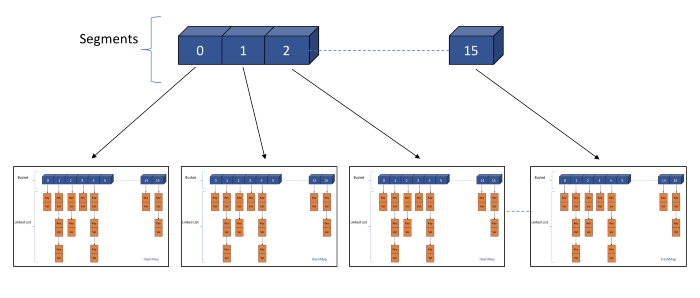
ConcurrentHashMap never locks the whole Map, instead it divides the map into segments and locking is done on these segments. ConcurrentHashMap is separated into different regions(default-16) and locks are applied to them. When setting data in a particular segment, the lock for that segment is obtained. This means that two updates can still simultaneously execute safely if they each affect separate buckets, thus minimizing lock contention and so maximizing performance.
Read, Write and Delete Operation in ConcurrentHashMap
- If one observes the above diagram, It is clear that whether it is Insertion or Read operation, one has to first identify the index of the segment where Insert/Read operation suppose to happen.
- Once that is identified then one has to identify the internal bucket/array of the hashmap to find the exact position for insertion/read.
- After identifying the bucket, iterate over the linked-list to check the key value pair.
- In case of insertion if key matches replace the value with the new one otherwise insert the key with value at the end of the linked-list.
- In case of read wherever key matches retrieve the value and return that value. if no match then return null.
- In case of delete if the key matches delete the link corresponding to that key.
Simultaneous Read and Write operations by Multiple Threads on same or different segments of ConcurrentHashMap
- Read/Get Operation :- Two Threads T1 and T2 can read data from same or different segment of ConcurrentHashMap at the same time without blocking each other.
- Write/Put Operation :- Two Threads T1 and T2 can write data on different segment at the same time without blocking the other. But Two threads can’t write data on same segments at the same time. One has to wait for other to complete the operation.
- Read-Write Operation :- Two threads can read and write data on different segments at the same time without blocking each other. In general, Retrieval operations do not block, so may overlap with write (put/remove) operations. Latest updated value will be returned by get operation which is most recently updated value by write operation (including put/remove).
I think thats enough to understand working of ConcurrentHashMap.
Happy Coding .. :)